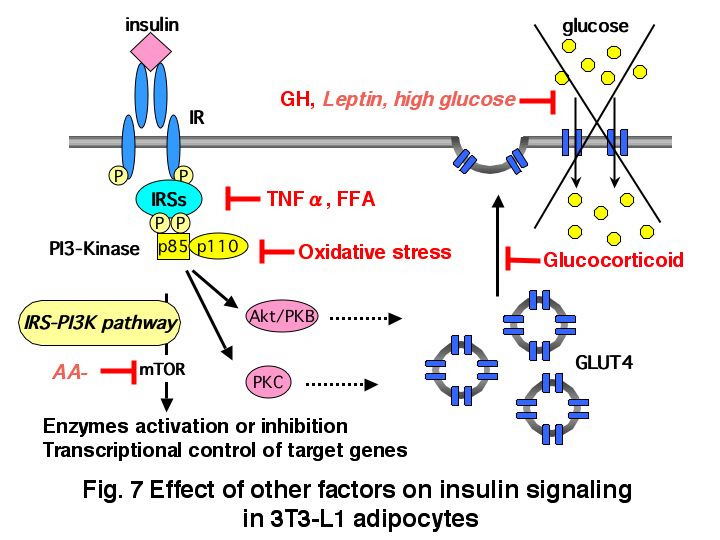
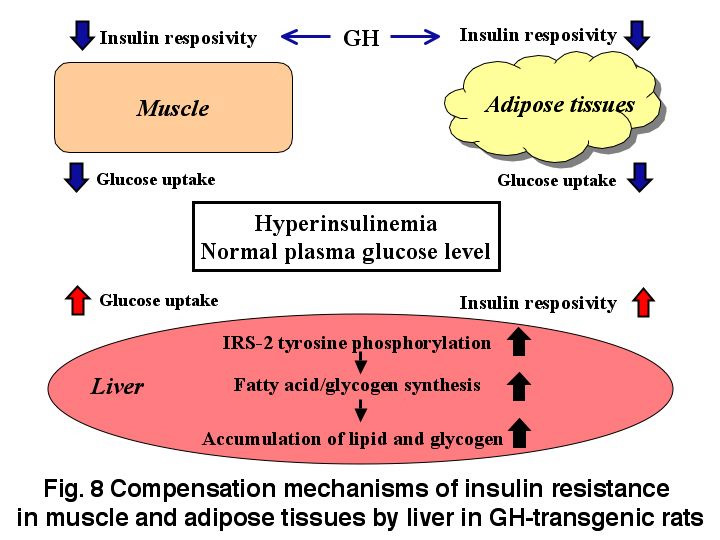
Growth hormone (GH) is well known to play important roles in regulating growth and metabolism. GH excess has been shown to lead to insulin resistance; however, the molecular mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Our results show that chronic GH treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes with GH reduces insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes despite normal glucose transporter (GLUT) 4 translocation to the plasma membrane (Fig. 7), suggesting that chronic GH treatment of adipocytes causes insulin resistance by novel mechanisms. On the other hand, the human GH transgenic (TG) rats that our colleagues developed, were characterized by high levels of serum hGH and IGF-I, resulting in an increase in body length and weight. These TG rats showed higher levels of plasma insulin compared to control littermates, whereas plasma glucose concentrations were normal. Insulin-dependent glucose uptake into adipocytes and muscle was impaired, suggesting that these rats developed insulin resistance. In contrast, insulin-independent glucose uptake into hepatocytes from TG rats was significantly increased, and glycogen and lipid levels in livers of TG rats were remarkably high. We then studied insulin signaling at early stages and insulin action in primary cultures of hepatocytes prepared from TG rats. We found that insulin-dependent IRS-2 tyrosine phosphorylation, glycogen synthase activation and expression of enzymes that induce lipid synthesis, were potentiated in hepatocytes of TG rats. These results suggest that impairment of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by GH excess in adipose tissue and muscle is compensated by up-regulation of glucose uptake in liver (Fig. 8).
We believe this compensation is very important for homeostasis. In addition, from the point of view of homeostasis, we are conducting a series of experiments to shed a light to the effect of various factors in the presence of IGF on growth, differentiation and apoptosis of various cells including adipocytes.